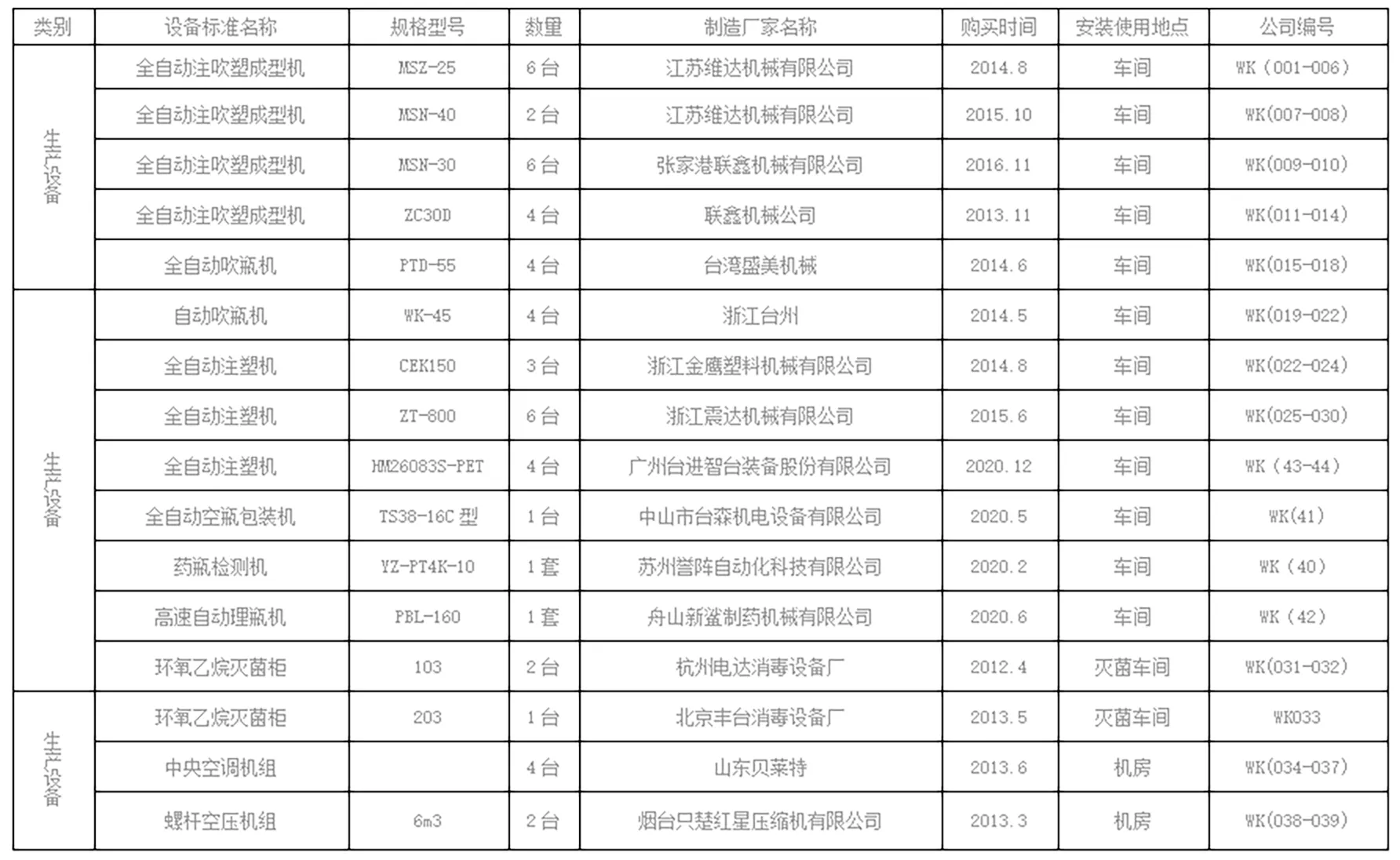
Applications of Petri Dishes in Microbiological Research and Laboratory Practices
Uses of Petri Dishes in Microbiology Laboratories
Petri dishes, also known as Petri plates, are essential tools in microbiology laboratories, serving a multitude of purposes that significantly aid research and experimentation
. Named after the German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri, these shallow, flat dishes are typically made from glass or clear plastic and are used primarily for cultivating and isolating microorganisms.One of the primary uses of Petri dishes is in the culture of bacteria and fungi. Microbiologists use them to grow a variety of microorganisms on nutrient-rich media, such as agar. Agar can be infused with specific nutrients that cater to the growth needs of certain bacteria, allowing for selective cultivation. For example, when culturing Escherichia coli, a nutrient agar enriched with yeast extract can be utilized. The transparent nature of the Petri dish also allows for easy observation of microbial growth, enabling scientists to analyze colony morphology and characteristics.
Petri dishes are also widely used in laboratory techniques such as streak plating. This method involves spreading a diluted sample across the surface of an agar plate to achieve isolated colonies. Streak plating is crucial for isolating pure cultures from mixtures, aiding in the identification and characterization of specific microorganisms. Furthermore, microbiologists can perform various biochemical tests directly on the growth media within a Petri dish, which helps in determining the metabolic capabilities of the cultured microorganisms.
uses of petri dish in microbiology laboratory
In addition to culture techniques, Petri dishes serve as a vital tool for antibiotic susceptibility testing. The disk diffusion method, commonly referred to as the Kirby-Bauer test, involves placing antibiotic-impregnated disks on an agar surface inoculated with a bacterial pathogen. After incubation, researchers can assess the effectiveness of antibiotics by measuring the zones of inhibition, which indicate bacterial resistance or sensitivity to specific antibiotics.
Another important application of Petri dishes is in the field of environmental microbiology. Researchers use them to study microbial populations in soil, water, and air samples by determining the types and quantities of microorganisms present in different environments. This information is critical for understanding ecological relationships and the impacts of pollutants.
In summary, Petri dishes are indispensable in microbiology laboratories due to their versatility and functionality. From culturing and isolating microorganisms to performing susceptibility testing and environmental analysis, these dishes play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of microbial life and its implications in various fields, including medicine, ecology, and biotechnology. Their widespread use continues to contribute significantly to scientific research and discovery.
-
Aesthetic Makeup Spray Bottles | Fine Mist Empty RefillableNewsAug.19,2025
-
White Plastic Veterinary Vaccine Vials | Lab Liquid BottlesNewsAug.18,2025
-
Plastic Medicine Liquid Bottle: Secure Flip Top Drug VialsNewsAug.17,2025
-
Durable 250ml Blue Plastic Vaccine Vial for Lab & Vet UseNewsAug.16,2025
-
Sterile Virus Sample Tubes: Secure & Reliable Specimen CollectionNewsAug.15,2025
-
White 250ml Plastic Vaccine Vial for Lab & Vet MedicineNewsAug.14,2025
























